To Prevent Tooth Loss from Periodontal Disease

What is Periodontal Disease?
There are many bacteria present in the mouth. The mass of bacteria called "biofilm" that adheres to the surface of the teeth is the cause of periodontal disease.
Brushing is done to remove the "biofilm," but if it remains attached, it causes inflammation of the gums, leading to the dissolution of the bone supporting the teeth, eventually resulting in tooth loss, which is a frightening disease.
It progresses without much pain, making it difficult to notice, and since the bone that has dissolved does not return to its original state, early detection before progression is important.
Periodontal Disease and Systemic Diseases
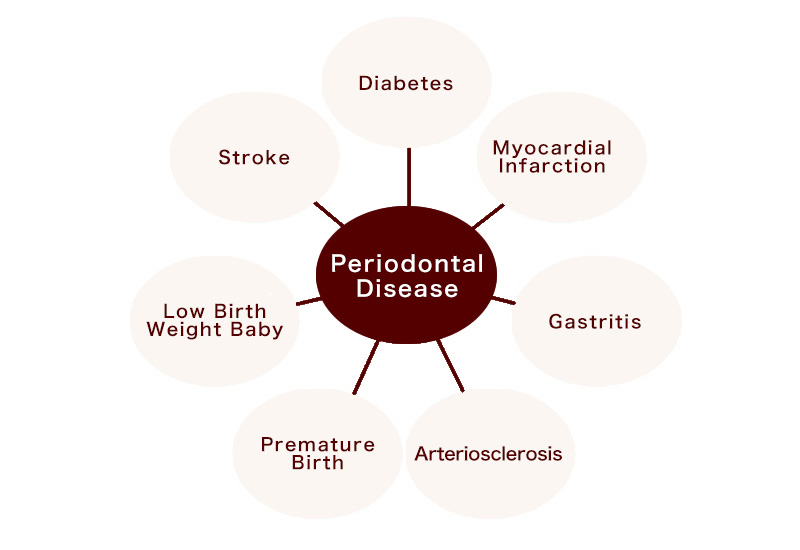
Periodontal disease is not just a problem of the "teeth." It is said that when one contracts periodontal disease, bacteria enter the body, affecting systemic diseases.
Conditions associated with periodontal disease include respiratory diseases, heart disease, diabetes, and premature birth or miscarriage during pregnancy.
It is also said that having diabetes makes one more susceptible to periodontal disease.
Periodontal Disease and Bad Breath
The main cause of bad breath is in the mouth.
One is the white coating on the tongue, and the other is the bacteria causing periodontal disease.
The main cause of bad breath is volatile sulfur compounds (hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan), but the bacteria causing periodontal disease produce a large amount of methyl mercaptan, which has a stronger odor than hydrogen sulfide. Therefore, people with periodontal disease have a characteristic strong bad breath.
Flow from Examination to Treatment
The frightening aspect of periodontal disease is that it progresses without much pain in the early and middle stages, and symptoms continue to advance. Pain and swelling symptoms appear only in the late stages, and until then, there are almost no subjective symptoms.
This is the most significant feature of this disease and also the scariest part.
Therefore, we check whether you are brushing properly and whether you have periodontal disease.
Except in cases of urgency, if there is a lot of bleeding, treatment begins with curing periodontal disease. We confirm whether proper brushing is being done and also perform teeth cleaning.
If there are many bacteria in the mouth, there is a possibility of recurring cavities even after cavity treatment. Also, if there is a lot of bleeding during treatment, it may not be possible to make precise fillings or take accurate impressions.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease - By Level -
Symptoms of Mild Gingivitis
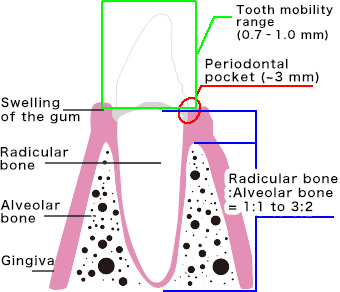
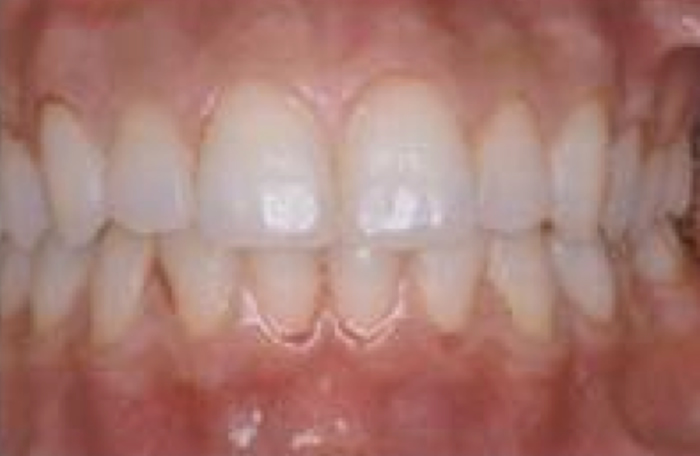
Mild bleeding is observed.
Gingivitis returns to a healthy state with proper oral hygiene and removal of plaque and tartar.
Symptoms of Moderate Gingivitis
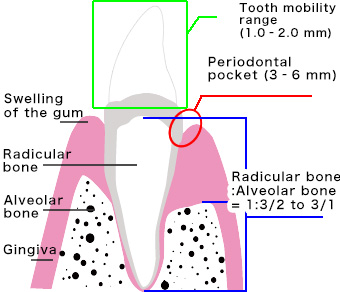
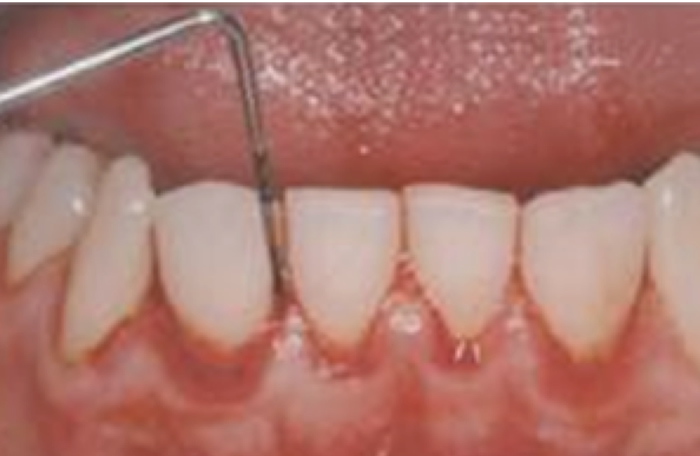
Characterized by a large amount of bleeding, redness, and swelling due to probing.
Symptoms of Severe Gingivitis
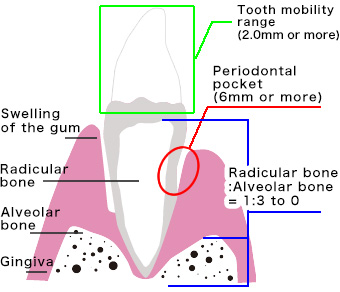
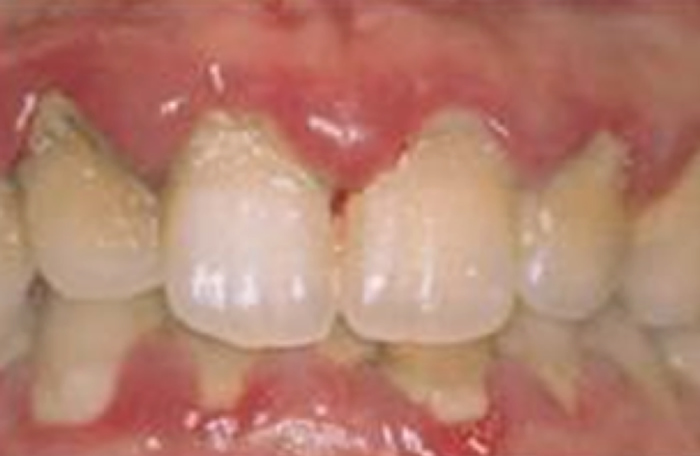
Characterized by spontaneous bleeding, redness, and swelling without probing.
Pseudo pockets are formed. The height of the gums increases on the crown side.
In the worst case, teeth may fall out.
Cases Where Tooth Extraction is Recommended Due to Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is a disease where the bone surrounding the teeth dissolves.
Symptoms of periodontitis include bad breath, pus discharge, tooth mobility, gum swelling, in addition to symptoms of gingivitis. If there is severe tooth mobility, pus discharge, swelling, pain, and inability to chew, tooth extraction may be necessary.
What is Regenerative Therapy?

Depending on the state of periodontal disease, healing may not be expected with initial treatment alone. In such cases, surgical procedures such as removing tartar and poor gums by peeling the gums may be performed.
In our clinic, we refer patients to periodontal specialists for regenerative therapy to regenerate periodontal tissues such as alveolar bone and gums.
Risks Associated with Treatment
Postoperative risks in regenerative therapy include infection due to the opening of sutures in the gums where autologous bone or artificial bone was transplanted.
General Dental Treatment
1 Protecting the Patient's Precious Teeth

Thorough consideration to ensure as little pain as possible for the patient
2 To Have a Long Relationship with Your Own Teeth

Specialized cleaning to protect important teeth with specialized preventive dentistry
3 Minimally Invasive Precision Treatment
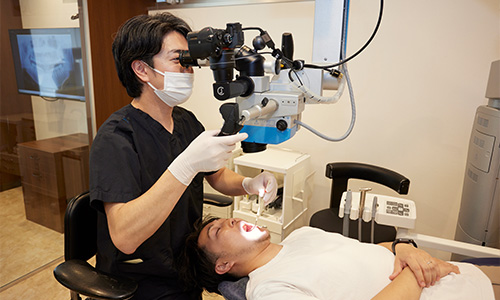
Direct bonding that minimizes cutting and reduces the number of treatment sessions
4 To Prevent Tooth Loss from Periodontal Disease
Periodontal treatment to protect the patient's teeth from periodontal disease, which causes tooth loss
5 Aiming to Preserve the Nerve as Much as Possible

To live with your own teeth for as long as possible...
Our clinic considers this in our treatments.